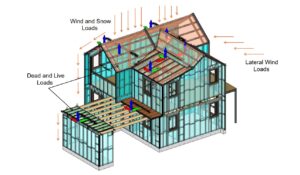
Images provided by Scottsdale Construction Systems
Cold-formed steel framing (CFS) for residential construction is increasing worldwide. Building professionals increasingly recognize steel’s high strength-to-weight ratio, non-combustibility, faster construction schedules and enhanced quality control for constructing buildings that are both resilient and sustainable.
However, CFS’s unique characteristics require careful planning and coordination throughout the design process. To assist engineers, Steel Framing Industry Association (SFIA) member Scottsdale Construction Systems published an article titled, “Steel Frame House: A Complete Guide to Best Engineering Practices.” This resource offers a comprehensive roadmap that helps engineers design CFS framed houses more efficiently.
5 Steps to Design CFS Homes
Scottsdale’s “Complete Guide to Engineering Practices” says that there are several “key obstacles engineers face when working with steel frame houses.”
To address these obstacles, Scottsdale offered five steps to follow when designing a home with CFS:
Step 1: Architectural Planning & Early Collaboration
Begin by gathering the approved architectural plans and assessing how to maximize the use of CFS framing. Engineers must work closely with architects, clients and manufacturers to finalize the design.
“Early collaboration among the entire project team allows for better optimization of material usage and greater structural design efficiency, all while ensuring that the client’s requirements are fully met,” says the Scottsdale guide.
Step 2: Load Flow Path Analysis
Once the architectural plans are finalized, define a clear load flow path for the steel framing system. This involves:
- Identifying the Framing System: Determine whether the project will use steel frames, trusses, joists or rafters, along with standard wall components such as studs, noggings and plates
- Calculating Loads: Compute live, wind, seismic and snow loads according to local codes, as well as dead loads based on the selected materials
- Establishing Load Transfer: Map out how these loads are transferred from the roof to the foundation, ensuring all factors are addressed for structural integrity and occupant safety
“Calculating the loads and defining the load path ensures no critical factors are overlooked during the design and construction of the steel frame house,” says the article.
Step 3: Preliminary Member Designation
Selecting the appropriate members and sizes for walls, roofs, floors and ceilings is crucial. Engineers should review the manufacturer’s catalog and prioritize standard sections to ensure timely procurement and a smoother construction process.
In cases where architectural plans require wider spans or heavier loads, alternative solutions such as composite CFS sections may be considered. Hot-rolled sections may be necessary for elements like garage openings or wide hallways.
Step 4: Structural Analysis and Engineering Design
After selecting preliminary member sizes, analyze and verify their adequacy to ensure compliance with all required standards. This process is essential for upholding structural integrity and safety throughout the project.
CFS design software from manufacturers streamlines the process by converting architectural plans into detailed fabrication models while simultaneously conducting engineering checks. This integrated approach boosts efficiency, minimizes errors and shortens project timelines.
“Sometimes, software packages can only detail the steel frame house based on architectural plans and generate shop drawings,” says the Scottsdale article. “When this happens, the design engineer must turn to external software for structural analysis and design checks.”
ScotSteel and ScotStruct offer an efficient alternative, streamlining these tasks and reducing the overall workload.
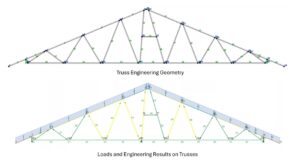
ScotSteel streamlines truss engineering by automatically generating precise engineering geometry and delivering comprehensive analysis results.
Step 5: Documentation and Certification
Comprehensive documentation and certification are essential for obtaining local approvals and guiding efficient construction. After finalizing the design, engineers prepare detailed layouts, calculation reports and other key documents, which typically include:
- Architectural layouts with member designations and legends
- Specifications for any non-standard elements
- Typical connection designs
- Quantity takeoff and bill of materials
- Detailed design calculation reports
- Design and inspection certifications
“The documentation process remains consistent globally, regardless of location or standards,” says the Scottsdale guide. “However, the sequence of steps and specific documentation may vary slightly based on regional rules and standards.”
Software Solutions
Scottsdale Construction Systems offers custom design and engineering software packages to support steel framed projects. Developed entirely in-house, the software packages ensure seamless compatibility with Scottsdale’s roll-forming machines, streamlining the transition from design to fabrication and enhancing overall project efficiency.
Read the full Scottsdale Construction Systems article.
About Scottsdale Construction SystemsScottsdale Construction Systems is a global company focused on research and development and the innovative development of light gauge steel technology for the house building and construction industries.
Scottsdale Construction Systems has been providing world leading solutions for the manufacture of steel frames and trusses for both the residential and commercial construction markets since its inception in 1995.
We are based in Australia and have North American operations and a rich history in the United States and North America. We have an established network here in North America and also in almost 100 countries worldwide.
For more information, visit scottsdalesteelframes.com.
Additional Resources
- Scottsdale Posts Comprehensive Guide to Steel Framing for Modern Construction
- SFIA’s Executive Director Highlights Cold-Formed Steel Innovations at Scottsdale-Sponsored Conference
- Australian Research Council and Scottsdale Fund CFS Floor Truss Research